STEAM Competence Framework for Educators
Spyropoulou, N., & Kameas, A. (2023). Augmenting the Impact of STEAM Education by Developing a Competence Framework for STEAM Educators for Effective Teaching and Learning. Education Sciences, 14(1), 25.
Acknowledging the multifaceted roles of STEAM educators, the STEAMComp Edu framework groups the competences into areas and the areas into perspectives. The framework features 41 core competences, organized in 14 distinct areas, and grouped under five perspectives. The framework notably highlights the crucial role of educator collaboration and community involvement, reflecting insights and needs directly expressed by educators. Organized hierarchically, it provides clear and comprehensive coverage, addressing educators’ varied roles, including instructional design, mentorship, and community engagement. The figure below provides the structure of the framework, including the perspectives, areas, and examples of competences.
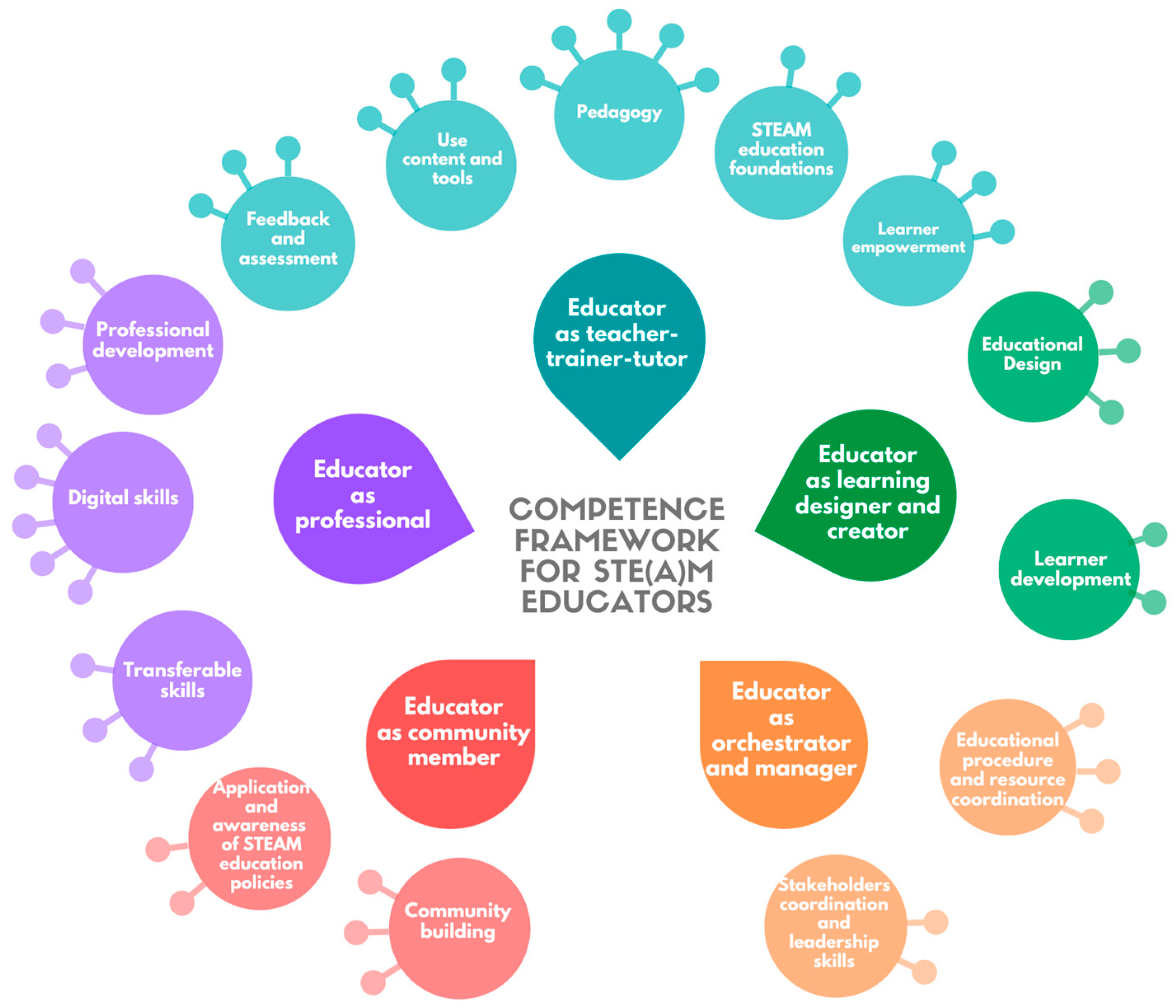
|klik voor vergroting | STEAM Educators’ Competence Framework Perspectives and Areas. Bron |
The STEAM educators’ roles represented by the five perspectives incorporated in STEAMComp Edu include:
- The educator’s role as a teacher-trainer-tutor encompasses the educator’s ability to facilitate effective student learning through mastery of pedagogical techniques, deep content knowledge, adeptness in instruction, proficient use of educational tools, and the capability to provide constructive feedback and assessment. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of empowering learners, fostering their autonomy, and guiding them toward academic success.
- The educator’s role as a learning designer and creator focuses on the design and development phase of the educational process. It requires competences related to planning, preparing, and developing educational procedures, learning activities tailored for diverse STEAM learning environments. Ιn addition, competences that focus on the educator’s ability to create a supportive environment that bolsters learners’ growth in STEAM domains are included in this role.
- The educator’s role as an orchestrator and manager involves competences related to managing and orchestrating educational procedures, content, digital technologies, lab equipment, and group learning activities among students and other educators.
- The educator’s role as a community member underscores the educator’s position within broader institutional and STEAM-related communities. It involves competences in networking, collaborating with peers, and actively participating in community initiatives. Additionally, it emphasizes the application of policies that champion STEAM education and sharing experiences and best practices within the community.
- The educator’s role as a professional provides competences related to educators’ own professional growth. It necessitates competences in continuous learning, staying updated with the latest in STEAM education, and refining transferable and digital skills essential for STEAM activities.

